Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body processes blood sugar (glucose). Glucose is a vital energy source for your body, but when you have diabetes, your body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use it effectively. Insulin is the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Types
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose), a key source of energy for the body. There are three primary types of diabetes, each with unique causes and characteristics:
1. Type 1 Diabetes
An autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This type of diabetes often requires insulin therapy and careful monitoring to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
:: Read More Too: Understanding Type 1 Diabetes
2. Type 2 Diabetes
The most common form of diabetes, type 2 is often linked to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, physical inactivity, and obesity. In this condition, the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough to maintain normal blood sugar levels. Adopting a balanced lifestyle, including strategies for managing diabetes with diet, can significantly improve outcomes for those with type 2 diabetes.
:: Read More Too: Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
3. Gestational Diabetes
A temporary condition that occurs during pregnancy due to hormonal changes, leading to high blood sugar levels. While gestational diabetes often resolves after childbirth, it can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life for both the mother and child.
If left unmanaged, diabetes can lead to serious complications, including damage to the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves. Regular monitoring, medication (if prescribed), and lifestyle modifications such as healthy eating, exercise, and stress management are critical for preventing these complications and maintaining quality of life.
Learn From This Book: The Diabetic Cookbook and Meal Plan
Whether you're managing type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes, understanding its underlying causes and focusing on proactive care—including dietary adjustments—can play a transformative role in your journey toward better health.
A. Causes of Diabetes and Its Dangers
Understanding the causes of diabetes and its potential dangers is essential for prevention and effective management. Diabetes is a complex condition with multiple contributing factors, depending on the type.
Causes of Diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes
This form of diabetes is primarily caused by genetic factors and autoimmune reactions, where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. While the exact trigger is unclear, a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors is believed to play a role.
- Type 2 Diabetes
The most common type of diabetes, it is largely linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and an unhealthy diet. Family history can also increase the risk. Managing this condition often involves lifestyle changes, including adopting a natural solution for managing blood sugar with Curalin or Protein Powder, alongside regular exercise and balanced nutrition.
- Gestational Diabetes
This temporary condition occurs during pregnancy due to hormonal changes that affect insulin sensitivity. Pre-existing risk factors, such as obesity or a family history of diabetes, can increase the likelihood of developing gestational diabetes.
Dangers of Diabetes:
If not well-managed, diabetes can lead to severe health complications:
- Heart Disease and Stroke
Chronically high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes. - Kidney Damage
Diabetes is a leading cause of kidney disease, as high glucose levels strain and impair kidney function, potentially leading to kidney failure. - Vision Problems
Prolonged high blood sugar can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, resulting in diabetic retinopathy, which may lead to vision loss or blindness if untreated. - Nerve Damage (Neuropathy)
Elevated glucose levels can damage nerves, causing symptoms such as pain, tingling, or numbness, particularly in the hands and feet. Severe cases may result in complications like infections or amputations.
While the causes and dangers of diabetes are serious, proactive management can significantly reduce risks. A focus on healthy lifestyle choices, including dietary adjustments and exploring natural solutions for managing blood sugar with Curalin or Protein Powder, can provide effective support for maintaining healthy glucose levels and preventing complications.
By addressing the root causes and dangers of diabetes, individuals can take charge of their health and minimize the impact of this chronic condition on their lives.
B. Symptoms of Diabetes
Recognizing the symptoms of diabetes early is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management. While symptoms can vary depending on the type of diabetes, here are some of the most common signs:
- Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination
High blood sugar levels cause the kidneys to work harder to filter and absorb excess glucose, leading to dehydration and increased thirst. Frequent urination is often a direct result. - Extreme Hunger, Even After Eating
When the body isn’t effectively using insulin, cells don’t get the energy they need, which can trigger persistent hunger despite eating regular meals. - Unexplained Weight Loss
In type 1 diabetes, the body may start breaking down fat and muscle for energy due to the lack of insulin. This can result in rapid and unexplained weight loss. - Fatigue and Irritability
Insufficient glucose in cells can leave you feeling constantly tired, while fluctuating blood sugar levels can contribute to irritability and mood changes. - Blurred Vision
High glucose levels can cause swelling in the lens of the eye, leading to vision issues. If left unmanaged, this can progress to more severe complications like diabetic retinopathy. - Slow-Healing Sores or Frequent Infections
Elevated blood sugar levels can impair circulation and weaken the immune system, making it harder for wounds to heal and increasing susceptibility to infections.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional immediately for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early detection can prevent or delay the onset of serious complications associated with diabetes, such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision loss.
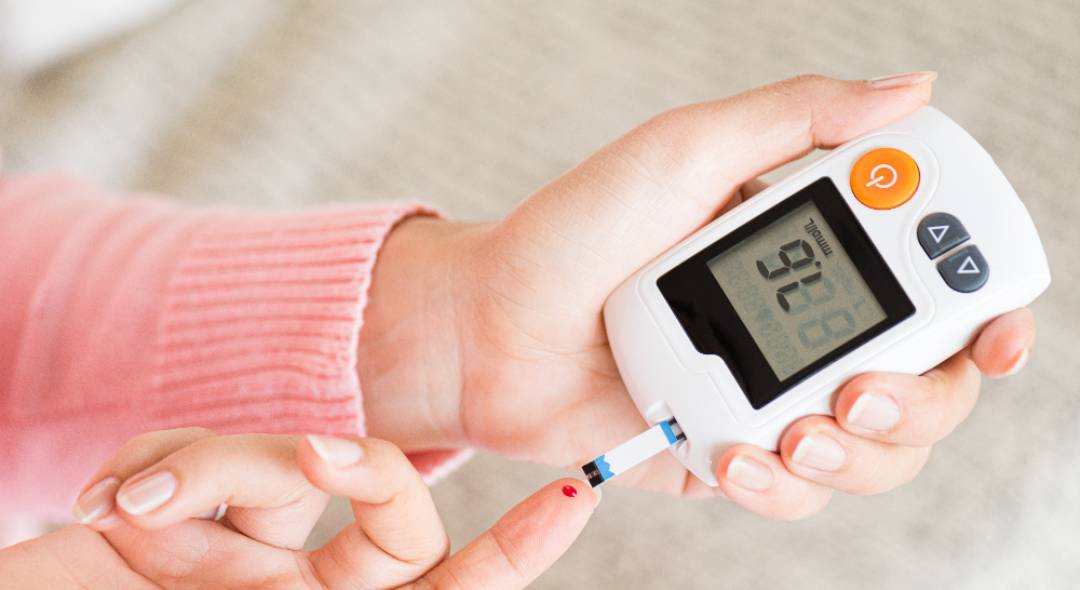
For those managing diabetes, regular monitoring using tools like blood glucose test strips is vital to track blood sugar levels and maintain control over the condition. Taking proactive steps and seeking medical advice promptly can significantly improve long-term outcomes.
Understanding these symptoms and responding quickly can make all the difference in effectively managing diabetes and maintaining overall health.
C. How to Prevent Diabetes
Preventing diabetes, especially type 2, involves making healthier lifestyle choices. Here are some effective strategies:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a major risk factor for diabetes, so keeping your weight in check is crucial.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Limit processed foods and sugary beverages.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity, like walking, swimming, or cycling, helps regulate blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: If you’re at risk, regular check-ups and monitoring can help detect prediabetes early.
D. How to Treat Diabetes
Managing diabetes involves a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and ongoing care:
- Medication or Insulin Therapy: Depending on the type of diabetes, you may need oral medications or insulin injections to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Healthy Eating Plan: Work with a dietitian to develop a diabetes-friendly meal plan. Focus on foods with a low glycemic index to prevent spikes in blood sugar.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity helps manage blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of complications.
- Monitor Blood Sugar: Use a glucometer to track blood sugar levels and ensure they stay within the recommended range.
- Regular Doctor Visits: Routine check-ups help monitor your overall health and prevent complications.
Worried about blood sugar accuracy? Learn how to choose the best glucose test strips for consistent and reliable results in our full guide.
Diabetes is a serious but manageable condition. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and potential risks can empower you to take proactive steps to prevent or manage it effectively. Whether it’s adopting a healthier lifestyle, monitoring blood sugar, or following a treatment plan, small changes can make a big difference.
By staying informed and working closely with healthcare professionals, you can lead a healthier, more balanced life despite the challenges of diabetes. Start today—your health is worth it!
.jpg)

